
Harnessing Cloud Computing for Small Business Growth and Innovation
Advertisment
Harnessing Cloud Computing for Small Business Growth and Innovation
Cloud Computing has emerged as a transformative force for small businesses, granting them access to sophisticated technology solutions previously reserved for larger corporations. By utilizing cloud services, small enterprises can boost operational efficiency, reduce overhead costs, and drive innovation. This article delves into the myriad benefits, applications, challenges, and best practices of Cloud Computing tailored specifically for small businesses.
1. Understanding Cloud Computing for Small Businesses
1.1. What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud Computing entails the delivery of computing services—including data storage, processing power, and software applications—via the internet. This model empowers small businesses to access resources on-demand, providing the flexibility and scalability they require.
1.2. Significance of Cloud Computing for Small Enterprises
For small businesses, Cloud Computing serves as a vital technological foundation essential for competing in today’s dynamic market. By adopting cloud solutions, these businesses can enhance agility, utilize powerful tools, and allocate resources more effectively.
Keywords: Cloud Computing, small businesses, technology solutions
2. Advantages of Cloud Computing for Small Businesses
2.1. Cost Efficiency
By leveraging Cloud Computing, small businesses can eliminate the hefty costs of traditional IT infrastructure, including expensive hardware and maintenance. The pay-as-you-go model allows businesses to only pay for the services they use, making it particularly advantageous for startups operating on tight budgets.
2.2. Scalability
As small businesses evolve, their IT requirements change. Cloud Computing allows companies to effortlessly scale their resources based on demand, ensuring they have the right tools without financial overcommitment.
2.3. Enhanced Collaboration
Cloud-based tools foster collaboration among team members, enabling document and application access from anywhere. This flexibility promotes teamwork and can lead to increased productivity and creativity.
2.4. Improved Data Security
Many cloud providers offer robust security measures that protect sensitive business information. These security features often surpass what small businesses can implement independently, enabling them to safeguard customer data and meet regulatory standards.
3. Key Applications of Cloud Computing for Small Businesses
3.1. Cloud Storage Solutions
Cloud storage services (e.g., Google Drive, Dropbox) provide secure, scalable storage options for small businesses. This capability allows them to store important files without the hassle of managing physical hardware.
3.2. Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Cloud-based CRM systems (e.g., Salesforce, HubSpot) enable small businesses to efficiently manage customer interactions and data. These tools streamline sales processes, enhance customer service, and support marketing efforts.
Advertisment
3.3. Project Management Tools
Cloud project management solutions (e.g., Asana, Trello) allow teams to collaboratively plan, execute, and monitor projects. These tools offer visibility into project progress, deadlines, and responsibilities, fostering accountability.
3.4. Financial Management Software
Cloud-based financial tools (e.g., QuickBooks, Xero) assist small businesses in managing their accounting, invoicing, and financial reporting. These tools automate many processes, alleviating administrative burdens and allowing owners to focus on growth.
Keywords: cloud storage, CRM, project management, financial management
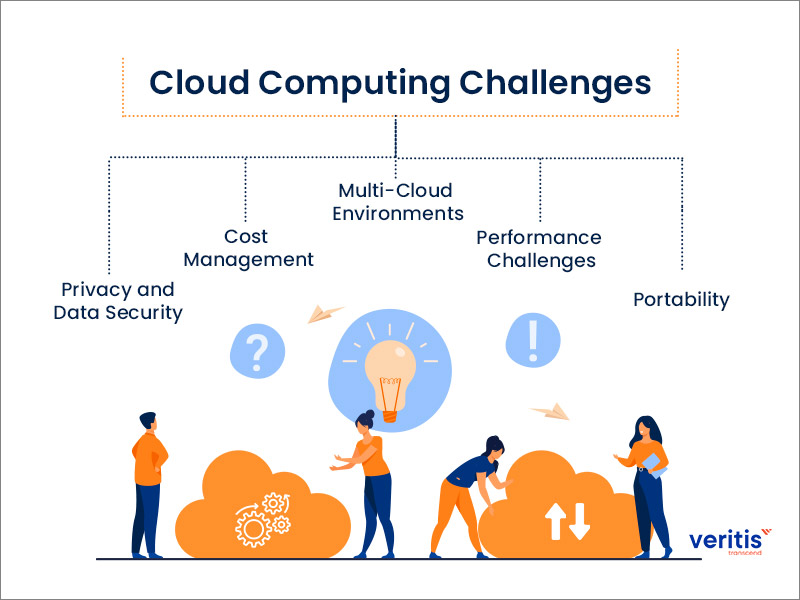
4. Challenges of Cloud Computing for Small Businesses
4.1. Data Security Concerns
Despite robust security measures from cloud providers, small businesses may still fear data breaches and unauthorized access. Selecting a reliable provider and understanding security protocols are essential steps to mitigate these risks.
4.2. Internet Dependence
Cloud Computing services rely heavily on stable internet connectivity. Businesses in areas with poor connectivity may face disruptions that can negatively impact operations and productivity.
4.3. Managing Multiple Services
As small businesses adopt various cloud solutions, managing multiple platforms can become a challenge. Ensuring seamless integration and a cohesive experience across different systems is vital for operational efficiency.
Keywords: data security, internet dependence, service management
5. Best Practices for Implementing Cloud Computing in Small Businesses
5.1. Assess Business Needs
Before implementing cloud solutions, small businesses should perform a comprehensive assessment of their specific requirements and goals. This evaluation will help identify which cloud services align best with their objectives.
5.2. Choose the Right Provider
Selecting a reputable cloud provider with experience in supporting small businesses is crucial. Evaluate providers based on their security measures, customer support, scalability options, and pricing structures.
5.3. Implement Strong Security Protocols
Establishing robust security measures is essential for safeguarding sensitive data. Small businesses should implement encryption, multi-factor authentication, and conduct regular security audits to protect their information.
5.4. Provide Employee Training
Offering training on effective use of cloud-based tools is vital for maximizing their potential. Educated employees can leverage Cloud Computing technologies to enhance productivity and streamline operations.
Keywords: assess needs, choose provider, security protocols, employee training
6. Conclusion
Cloud Computing empowers small businesses to enhance efficiency, cut costs, and drive innovation. By embracing cloud technologies, small enterprises can compete more effectively and respond swiftly to market changes. Understanding the challenges and implementing best practices will enable small businesses to harness Cloud Computing for sustainable growth and long-term success.
Advertisment










Post Comment