
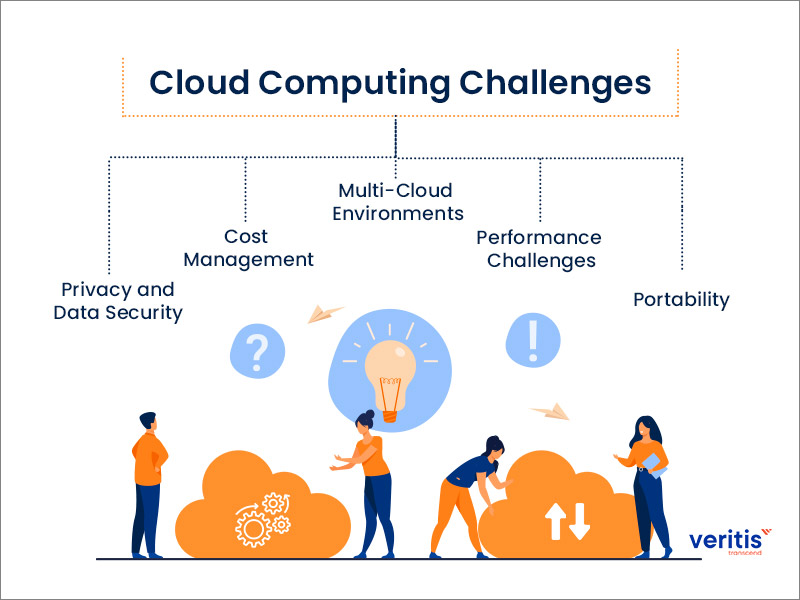
Key Challenges of Cloud Computing: What Businesses Need to Know
Advertisment
Cloud computing has become an essential part of modern business operations, offering benefits like scalability, cost efficiency, and enhanced collaboration. However, like any technology, cloud computing comes with its own set of challenges. Understanding these challenges is critical for businesses looking to optimize their cloud infrastructure and avoid potential pitfalls.
In this article, we will explore the key challenges associated with cloud computing, providing businesses with insights on how to overcome these hurdles effectively.
- Security and Privacy Concerns
One of the most prominent challenges in cloud computing is ensuring data security and privacy. Storing sensitive business information on third-party servers makes it vulnerable to breaches, hacking, and other forms of cyberattacks.
Data Breaches: Cloud environments are prime targets for cybercriminals. Inadequate security measures can result in data breaches that expose sensitive customer or business data, damaging a company’s reputation and finances.
Data Privacy Regulations: Cloud providers operate globally, and different regions have different data privacy regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe or the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States. Ensuring compliance with these regulations is a significant challenge for businesses operating in the cloud.
How to Overcome It: Businesses should adopt a zero-trust security model, implement end-to-end encryption, and ensure that their cloud provider complies with relevant privacy regulations. Regular security audits and employee training can also help strengthen security.
- Downtime and Service Reliability
While cloud providers offer high levels of availability, no system is completely immune to downtime. Service outages can disrupt operations, leading to productivity loss, financial costs, and customer dissatisfaction.
Outage Risks: Even the most reliable cloud providers can experience downtime due to technical glitches, maintenance, or large-scale cyberattacks, as seen in past incidents with Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Google Cloud.
Dependency on Providers: Businesses that rely heavily on cloud services may have little control over such downtimes, creating potential bottlenecks in their operations.
How to Overcome It: To mitigate downtime risks, businesses should implement multi-cloud or hybrid cloud strategies, distributing workloads across multiple cloud providers to ensure redundancy. Additionally, having a strong disaster recovery plan is essential to minimize the impact of outages.
- Cost Management and Control
Although cloud computing can be cost-effective, managing and controlling cloud expenses can be challenging. Businesses often underestimate the costs associated with cloud storage, data transfer, and computing resources, leading to budget overruns.
Unforeseen Costs: Hidden fees such as data egress charges (costs for moving data out of the cloud) or over-provisioning resources can inflate cloud expenses.
Scalability Costs: While scaling up in the cloud is easy, businesses may end up paying for unused resources if they do not have proper monitoring and scaling practices in place.
How to Overcome It: Businesses should adopt cloud cost management tools and monitor usage in real-time to avoid over-provisioning. Regularly reviewing pricing models and optimizing cloud workloads based on business needs can also help control costs.
- Compliance and Regulatory Issues
Compliance with industry standards and regulations is a critical challenge in cloud computing. Different industries have specific regulations that must be adhered to, and moving data to the cloud does not exempt businesses from these requirements.
Industry-Specific Regulations: Sectors like finance, healthcare, and government have stringent regulations, such as HIPAA for healthcare data or PCI DSS for payment processing. Ensuring that cloud providers meet these regulatory requirements is essential for avoiding fines and legal issues.
Advertisment
Data Residency: Some regions mandate that data must be stored within specific geographic locations, posing challenges for businesses that operate across multiple jurisdictions.
How to Overcome It: Before migrating to the cloud, businesses should thoroughly evaluate their compliance needs and ensure that their chosen cloud provider supports the necessary regulatory requirements. Additionally, legal teams should be involved to ensure contracts cover compliance obligations.
- Lack of Control and Flexibility
One of the concerns for businesses using cloud services is the lack of direct control over their infrastructure. Since cloud services are managed by third-party providers, organizations may have limited control over how their data is handled, stored, and processed.
Vendor Lock-In: Moving data and applications from one cloud provider to another can be challenging due to compatibility issues and proprietary technologies. This vendor lock-in reduces flexibility and can make it difficult to switch providers if service quality declines or costs increase.
Customizability: Cloud services are designed to cater to a broad range of industries, which may limit customization options for businesses with highly specialized needs.
How to Overcome It: To maintain flexibility, businesses should invest in multi-cloud or open-source cloud solutions, which provide greater control over their infrastructure. Negotiating clear exit clauses in contracts can also help mitigate the risks of vendor lock-in.
- Data Transfer and Latency Issues
Transferring large amounts of data between cloud environments and on-premises systems can present significant challenges, particularly in terms of latency and bandwidth.
Latency: Cloud services can suffer from delays due to geographical distance between the data source and the data center, affecting real-time processing applications such as video conferencing, online gaming, and IoT services.
Bandwidth Limitations: Moving data across cloud providers or from cloud to on-premises systems can consume large amounts of bandwidth, resulting in higher operational costs and slower performance.
How to Overcome It: Businesses can use edge computing to process data closer to the source, reducing latency. Additionally, optimizing data transfer protocols and selecting cloud providers with data centers near their user base can help improve performance.
- Skills Gap and Expertise Shortage
The rapid growth of cloud computing has outpaced the availability of skilled professionals, creating a significant skills gap in the industry. As cloud technologies evolve, businesses face challenges in finding qualified personnel to manage and optimize their cloud environments.
Shortage of Expertise: Managing complex cloud infrastructures requires expertise in various areas, including security, architecture, and compliance. The shortage of such professionals can hinder a business’s ability to leverage cloud computing to its full potential.
Continuous Learning: Cloud technology is constantly evolving, and IT teams must stay up-to-date with the latest advancements, which requires continuous learning and training.
How to Overcome It: To address the skills gap, businesses should invest in employee training programs and consider outsourcing cloud management to managed service providers (MSPs). Additionally, leveraging automation tools can reduce the need for hands-on management of cloud infrastructure.
Conclusion
While cloud computing offers immense benefits, businesses must navigate several key challenges to fully leverage its potential. By addressing security concerns, managing costs, ensuring compliance, and overcoming latency and expertise gaps, organizations can optimize their cloud environments and drive innovation. As cloud technology continues to evolve, businesses that proactively address these challenges will be better positioned to succeed in the competitive digital landscape.
Advertisment










Post Comment